TRASH TALK

PSSST! Have you heard? You might be one of many people who can’t tell the difference between food waste and residual waste! No need to fear, Trash Talk is here! Below is a dictionary of terms that can help you along your responsible waste generation journey.

Word of The Day
RECYCLING
The process of collecting and breaking down waste to turn into new, usable materials.
EX.
Plastic Bottles → Backpack / Ecoboard /Furniture
Old Notebooks → Recycled Paper

TERMS YOU PROBABLY GET WRONG

TYPES OF WASTE

Biodegradable Waste
Non-hazardous materials that can naturally decompose.
Greenhouse Gas
Gases, such as carbon dioxide in methane, which trap heat in the atmosphere.
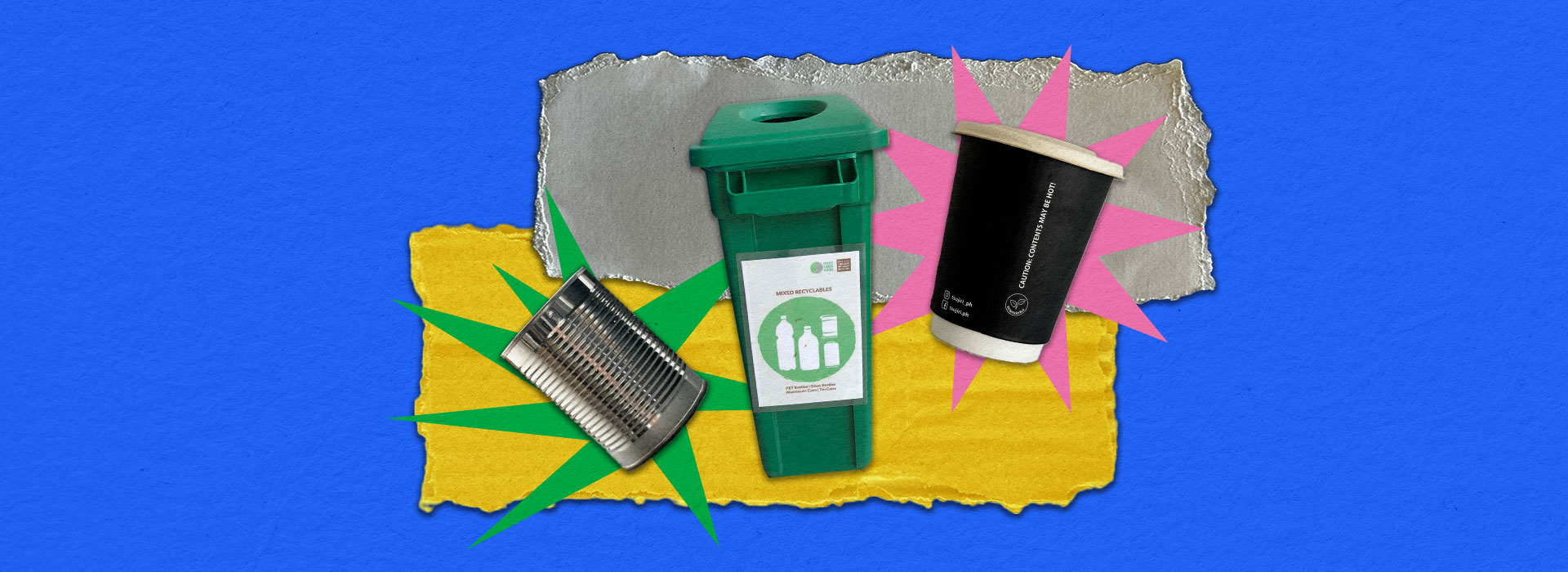

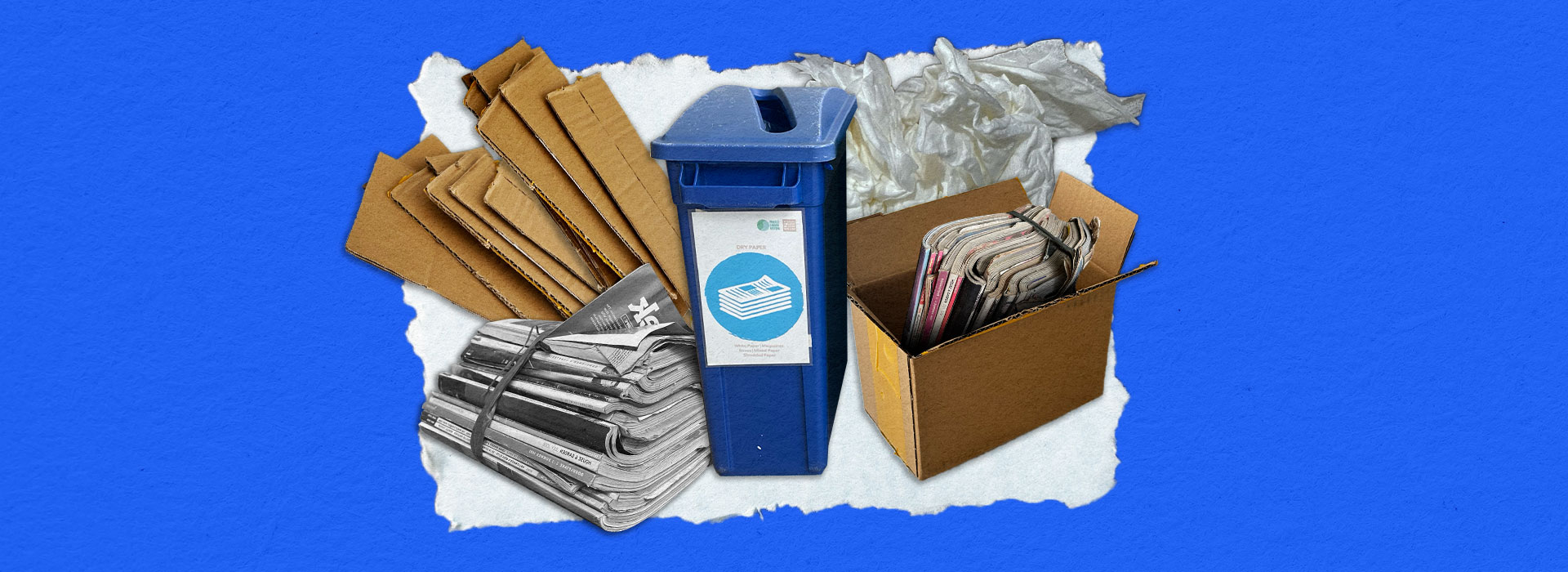
Recyclable Waste
Materials that can be processed into new, usable materials.
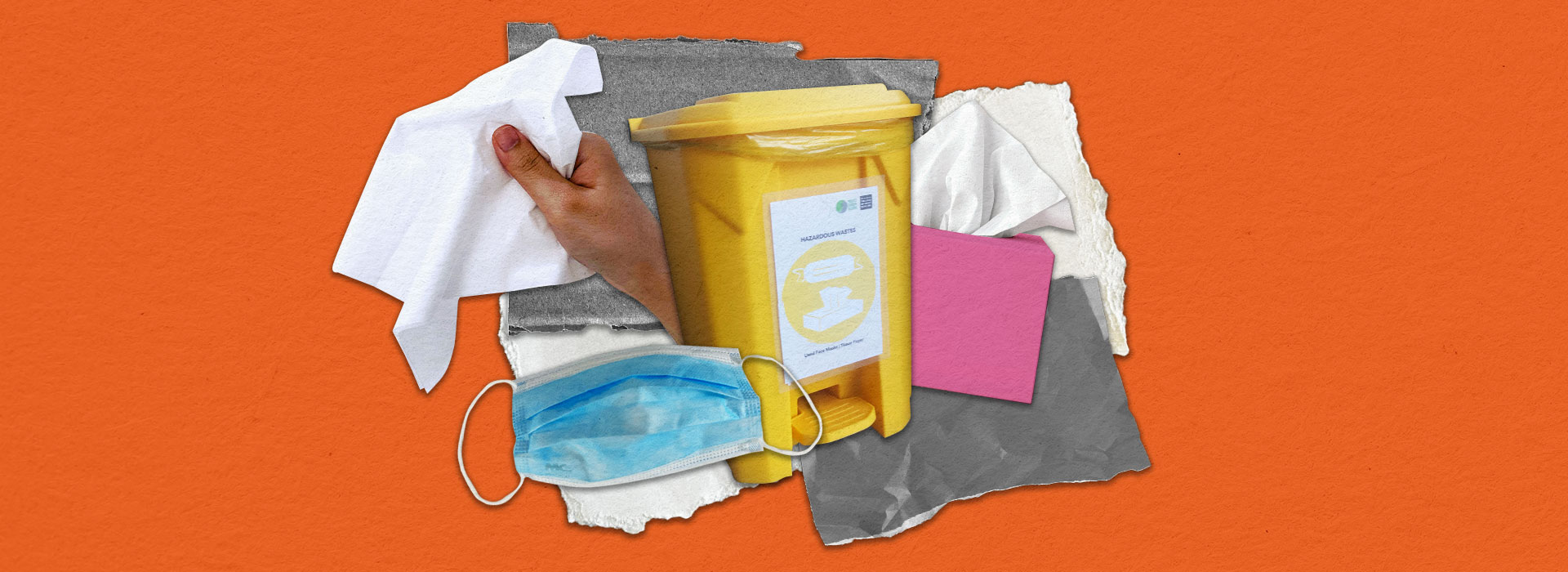

Hazardous Waste
They’re any waste produced that’s dangerous to human health or the environment.
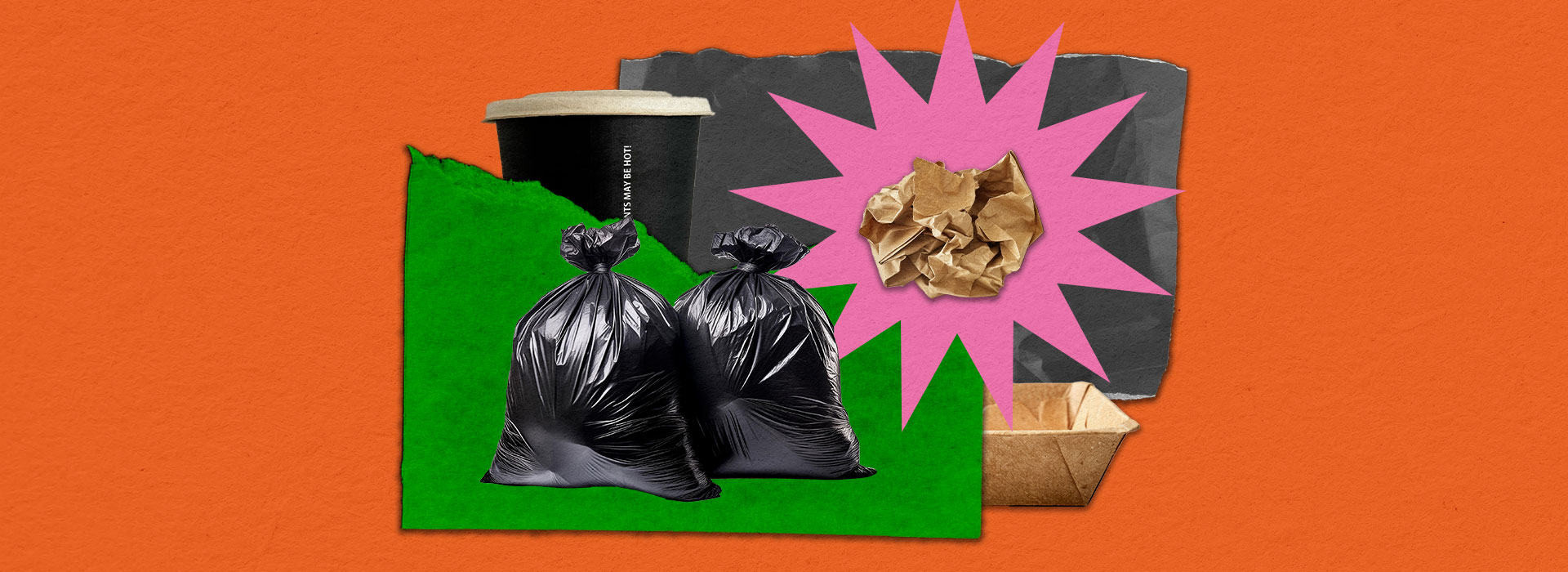

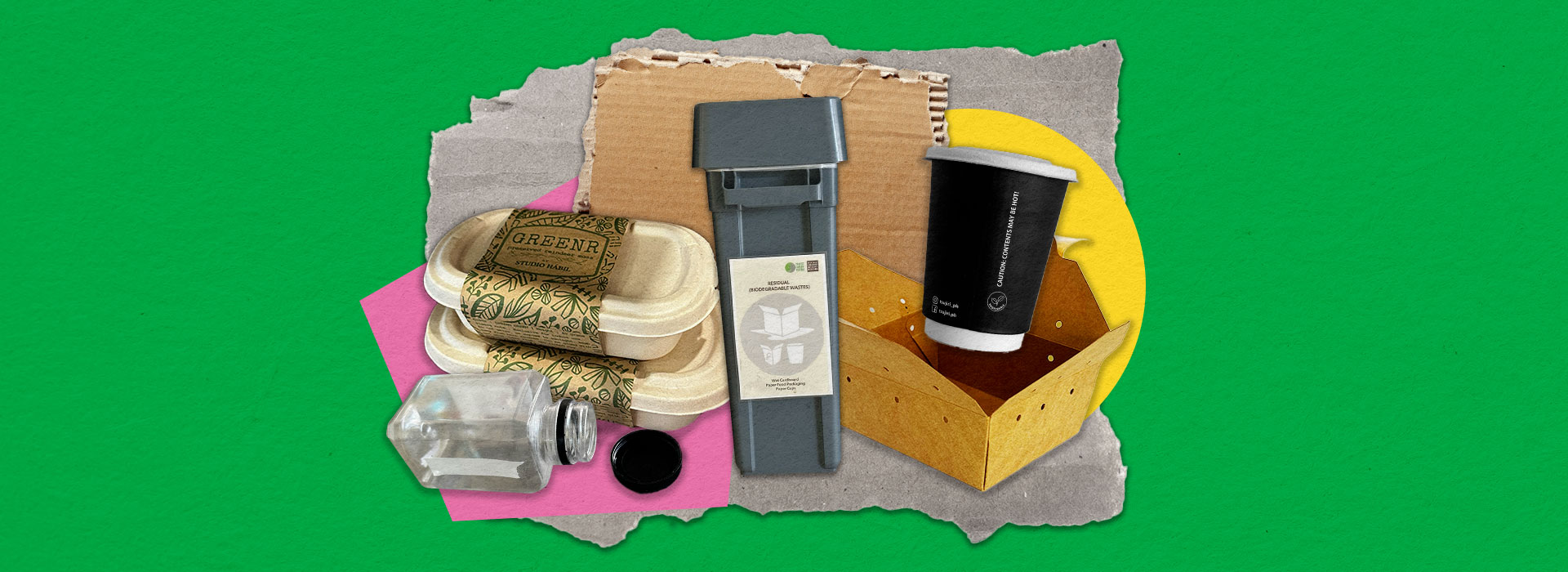
Residual Waste
Non-hazardous materials that cannot be recycled.
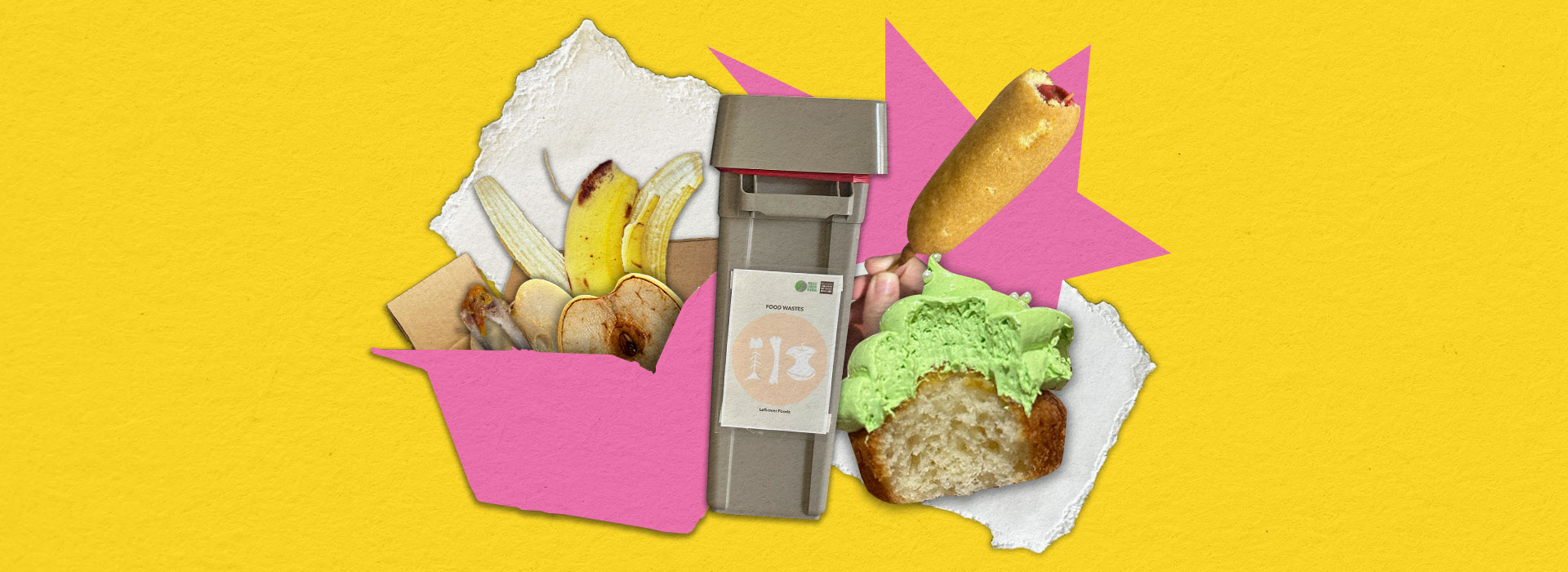

Food Waste
Solid leftovers excluding food containers, packaging, wrappers, and utensils.

Non-Biodegradable Waste
Non-hazardous materials that cannot naturally decompose and stay in-tact for years beyond their disposal.
WASTE MANAGEMENT

Compost
The natural process of recycling organic materials (food scraps, cardboard, leaves, etc.) to produce fertilizer, through speeding up decomposition.

Dump Site
Not to be confused with landfills; an open area where garbage is thrown but not managed or dealt with.

Landfill
Big sites housing solid waste for disposal. They’re intentionally engineered and managed to contain garbage and reduce the toxins produced.

Recycling
The process of collecting and breaking down waste to turn into new, usable materials.
EX.
Plastic Bottles → Backpack / Ecoboard / Furniture
Old Notebooks → Recycled Paper

Waste Segregation
The sorting of waste into different categories to allow for proper recycling and further disposal.

Upcycling
Upcycling
The act of repurposing or refurbishing an item that would otherwise be thrown away.
EX.
Tin Can → Planter
Glass Bottle → Flower Vase
ENVIRONMENTAL LINGO

Environmental Footprint
The measure of one’s positive and negative impact on the environment.

Greenhouse Gas
Gases, such as carbon dioxide in methane, which trap heat in the atmosphere.

Sustainability
To be able to maintain a process continuously and renewably over time. These are balanced practices and systems meeting our present needs that won’t compromise the future generations.


